A little bit little bit of distance could make all of the distinction. That’s what two researchers on the College of Sydney Nano Institute lately concluded in their research on a brand new methodology for “superlensing,” a means of seeing issues which can be smaller than the wavelength of sunshine, and doing so with none precise lenses.
The researchers discovered a brand new option to crash by way of the diffraction restrict, which prevents you from discerning any characteristic smaller than the wavelength of the sunshine that displays off it. Options smaller than which can be encoded solely in what are known as evanescent waves, which have amplitudes that die off exponentially and are virtually utterly misplaced inside a couple of wavelength.
Beforehand, evanescent waves have been detected by inserting a photoconductive probe proper subsequent to the item being imaged, which may distort the outcomes. It had been assumed that when the probe is just too removed from the item—even a tenth of the wavelength farther again—the sub-wavelength info is totally misplaced. “We realized that it’s not misplaced. It’s simply actually, actually dim,” says creator Boris Kuhlmey.
To regain that high-resolution info, researchers must amplify the dim sign with a superlens, product of specifically engineered metamaterials. However as a substitute of a bodily lens, Kuhlmey and co-author Alessandro Tuniz used numerical calculations to attain the identical consequence. They measured tiny fluctuations within the electromagnetic area brought on by the evanescent waves and just about amplified these by making use of equations that describe how the waves die out. Then, they might reconstruct the unique area throughout post-processing, attaining a decision one-fourth the scale of the diffraction restrict.
What issues, says Kuhlmey, is just not the precise know-how they used however the skill to choose up high-resolution info farther from the pattern than had been thought attainable, even with out a superlens.
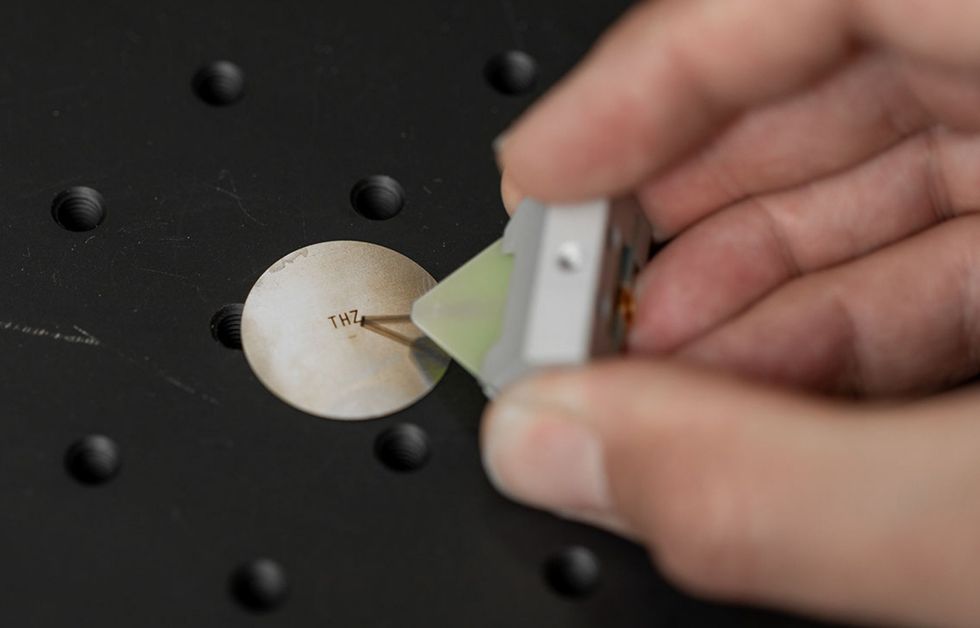 A researcher demonstrates how a photoconductive antenna scans the pattern, which measures lower than 4 millimeters throughout and has options as small as 0.15 millimeters. The College of Sydney
A researcher demonstrates how a photoconductive antenna scans the pattern, which measures lower than 4 millimeters throughout and has options as small as 0.15 millimeters. The College of Sydney
That’s essential as a result of they have been working with wavelengths of round one millimeter, which is within the terahertz frequency vary. And though bodily superlensing has been demonstrated in different frequencies, it has not been achieved her.
The terahertz area of the spectrum is a comparatively new space of analysis, partly as a result of the frequencies are too excessive for use with electronics and too low for photonics, says Kuhlmey. However such frequencies might be essential in organic analysis, as a result of water’s sturdy absorbency of terahertz frequencies, and for peering by way of the ceramic coatings used on semiconductor chips, amongst different issues. “In each a part of the spectrum, you discover new physics,” says Kuhlmey.
Tuniz and Kuhlmey word that their methodology is just not the primary to interrupt by way of the diffraction restrict, nor does it symbolize the very best decision achieved. Different strategies, comparable to these utilizing a really shut probe, supply higher decision. However that decision comes at a price. These strategies are gradual and may solely be used to scan small areas. “We’re including to the library of accessible high-resolution strategies that somebody might contemplate,” says Tuniz.
To realize high-resolution terahertz imaging with out superlensing, Tuniz and Kuhlmey must place an costly probe lower than a millimeter away from the pattern being noticed. Tuniz was all the time afraid of scraping the instrument towards that pattern and damaging both object. To make issues worse, the probe can distort the very area it’s there to measure. Alternately, utilizing a bodily lens to amplify the evanescent waves blocks out among the gentle. By performing superlensing just about, researchers get rid of that loss. “It’s area of interest, in a way, however laboratories everywhere in the world have tools comparable to this to grasp actually sophisticated issues,” says Tuniz.
“There will likely be actually stunning functions,” provides Kuhlmey, although he acknowledges that it’s unlikely to revolutionize microscopy as a complete.
In truth, the post-processing central to the Australian strategy is much like strategies routinely utilized in different areas of microscopy, based on Durdu Guney who research superlensing at Michigan Technological College. Though the applying to terahertz imaging is new, Guney says, “conceptually, I believe the thought is just not very novel.” His analysis has used related strategies in larger optical frequencies, for which superlensing is extra superior. Guney additionally questions whether or not the strategy will likely be efficient for extra sophisticated objects, among the options of which can be overwhelmed by noise.
After the analysis was revealed, Tuniz and Kuhlmey discovered that it had been posted on social media, the place commenters made joking allusions to a trope in police procedural TV reveals during which the characters “improve” blurry CCTV footage to disclose a key element. Utilizing actual ideas of physics, Tuniz acknowledges that the tip result’s fairly related.
“It’s turning the absurdity right into a actuality.”
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet

