A imaginative and prescient for future processors with practically double the density of transistors is starting to take form, now that each one three superior chipmakers have demonstrated CFETS, or complementary field-effect transistors. CFETs are a single construction that stacks each the sorts of transistors wanted for CMOS logic. On the IEEE Worldwide Electron Units Assembly this week in San Francisco, Intel, Samsung, and TSMC confirmed what progress they’ve made towards the following evolution in transistors.
Chip firms are transitioning from the FinFET gadget construction in use since 2011 to nanosheet, or gate-all-around, transistors. The names replicate the fundamental construction of the transistor. Within the FinFET, the gate controls the movement of present by means of a vertical silicon fin. Within the nanosheet gadget, that fin is reduce right into a set of ribbons, every of which is surrounded by the gate. The CFET primarily takes a taller stack of ribbons and makes use of half for one gadget and half for the opposite. This gadget, as Intel engineers defined within the December 2022 subject of IEEE Spectrum, builds the 2 sorts of transistor—nFETs and pFETs—on high of one another in a single, built-in course of.
Specialists estimate CFETs to roll out commercially seven to 10 years from now, however there may be nonetheless a variety of work earlier than they’re prepared.
Intel’s inverter
Intel was earliest of the three to exhibit the CFET, unveiling an early model at IEDM again in 2020. This time round, Intel is reporting a number of enhancements surrounding the only circuit that the CFET makes, an inverter. A CMOS inverter sends the identical enter voltage to the gates of each gadgets within the stack and produces an output that’s the logical inverse of the enter.
“The inverter is finished on a single fin,” Marko Radosavljevic, principal engineer at Intel’s parts analysis group, informed reporters forward of the convention. “At most scaling, it might be 50 %” of the dimensions of an unusual CMOS inverter, he mentioned.
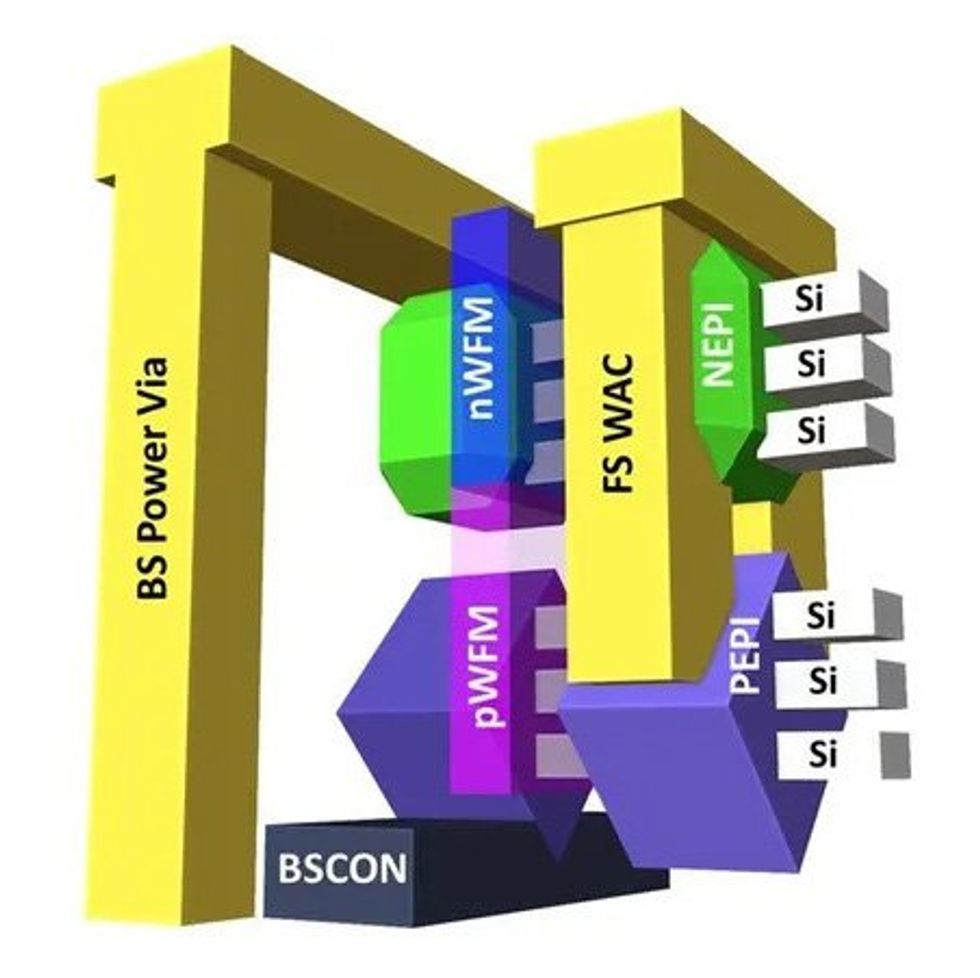 Intel’s inverter circuits depend upon a brand new manner of connecting the highest and backside transistors [yellow] and on contacting one among them from beneath the silicon [grey]Intel
Intel’s inverter circuits depend upon a brand new manner of connecting the highest and backside transistors [yellow] and on contacting one among them from beneath the silicon [grey]Intel
The hitch is that squeezing in all of the interconnects wanted to make that two-transistor stack into an inverter circuit eats away on the space benefit. To maintain issues tight, Intel tried to take away among the congestion concerned in connecting to the stacked gadget. In at present’s transistors, all of the connections come from above the gadget itself. However later this yr, Intel is deploying a know-how referred to as bottom energy supply that enables interconnects to exist each above and beneath the floor of the silicon. Utilizing that know-how to contact the underside transistor from beneath as a substitute of from above considerably simplified the circuit. The ensuing inverter had a density high quality referred to as contacted poly pitch (CPP, primarily the minimal distance from one transistor gate to the following) of 60 nanometers. At the moment’s 5 nm node chips have a CPP of about 50 nm.
Moreover, Intel improved the CFET stack’s electrical traits by growing the variety of nanosheets per gadget from two to a few, reducing the separation between the 2 gadgets from 50 nm to 30 nm, and utilizing an improved geometry for connecting elements of the gadget.
Samsung’s secret sauce
Samsung went even smaller than Intel, exhibiting outcomes for 48-nm and 45-nm contacted poly pitch (CPP), in comparison with Intel’s 60 nm, although these have been for particular person gadgets, not full inverters. Though there was some efficiency degradation within the smaller of Samsung’s two prototype CFETs, it wasn’t a lot, and the corporate’s researchers imagine manufacturing course of optimization will deal with it.
Essential to Samsung’s success was the flexibility to electrically isolate the sources and drains of the stacked pFET and nFET gadgets. With out enough isolation, the gadget, which Samsung calls a 3D stacked FET (3DSFET), will leak present. A key step to reaching that isolation was swapping an etching step involving moist chemical compounds with a brand new sort of dry etch. That led to an 80 % increase within the yield of fine gadgets.
Like Intel, Samsung contacted the underside of the gadget from beneath the silicon to avoid wasting house. Nevertheless, the Korean chipmaker differed from the American one by utilizing a single nanosheet in every of the paired gadgets, as a substitute of Intel’s three. Based on its researchers, growing the variety of nanosheets will improve the CFET’s efficiency.
TSMC takes its shot
Like Samsung, TSMC too managed to get to an industrially-relevant pitch of 48 nm. Its gadget’s distinctions included a brand new option to type a dielectric layer between the highest and backside gadgets to maintain them remoted. Nanosheets are typically shaped from alternating layers of silicon and silicon germanium. On the acceptable step within the course of, a silicon-germanium particular etching methodology removes that materials, releasing the silicon nanowires. For the layer destined to isolate the 2 gadget from one another, TSMC used silicon germanium with an unusually excessive fraction of germanium, understanding that it might etch away sooner than the opposite SiGe layers. That manner the isolation layer might be constructed a number of steps earlier than releasing the silicon nanowires.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet

